
You now have access to barrier coating for paper that is both eco-friendly and easy to use. In recent years, demand for sustainable solutions has surged, with companies and consumers seeking alternatives to traditional plastic coatings. This shift stems from stronger environmental regulations, changing consumer preferences, and new technologies that improve safety and efficiency. When you choose green coatings, you support a cleaner planet and benefit from advances that make application simpler than ever.
Key Takeaways
- Barrier coatings protect paper packaging from moisture, grease, and gases, extending its use and improving print quality.
- Green barrier coatings use renewable, biodegradable materials that reduce plastic waste and support recycling.
- Water-based and biopolymer coatings are popular green options that offer strong protection and are safe for food contact.
- Different coating types like biowax, hybrid, and marine biodegradable coatings suit various packaging needs and environmental goals.
- Applying green coatings can be done with common methods like roll, spray, and curtain coating, fitting both small and large-scale production.
- Green coatings now match or exceed traditional coatings in moisture and grease resistance while improving recyclability.
- Choosing the right coating depends on product needs, sustainability goals, and regulatory compliance to ensure performance and eco-friendliness.
- Innovations in materials and technology continue to improve green coatings, helping businesses stay competitive and environmentally responsible.
What Are Barrier Coatings?
Purpose and Function
You rely on paper for many packaging needs, but paper alone cannot always protect products from moisture, grease, or gases. Barrier coating for paper solves this problem by adding a thin, protective layer to the surface. This layer improves the performance of paper packaging and extends its range of uses.
- Barrier coatings increase resistance to moisture, gas, water, oil, and grease.
- They address the natural limitations of paper, making it suitable for packaging perishable goods such as seafood, fruits, and frozen foods.
- These coatings improve print quality, allowing you to achieve vibrant and clear graphics on packaging.
- You can enhance the visual appeal of your packaging with the right coating.
- Barrier coating for paper supports sustainability by enabling recyclable and environmentally friendly packaging solutions.
Tip: When you choose a barrier coating for paper, you help reduce the need for plastic and support a circular economy.
Common Applications
You see barrier coatings in action every day, especially in the food industry. Companies use these coatings to keep food fresh and safe, replacing traditional plastics and reducing environmental waste. The coatings make paper packaging impermeable to grease, oil, and gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide, which helps preserve food quality.
- Food packaging uses barrier coatings to meet food contact compliance and provide heat sealability.
- Consumer product packaging relies on these coatings to protect against solvents, oils, and fatty acids.
- Quick-serve packaging, such as coffee cups and sandwich wraps, benefits from grease resistance and moisture protection.
You find barrier coatings widely used in packaging for perishable foods, frozen foods, dairy products, and bakery items. These coatings ensure that your packaging maintains its integrity and protects the contents inside.
Note: By using barrier coatings, you can offer packaging that meets both performance and sustainability goals.
Why Go Green?

Environmental Impact
You face growing pressure to reduce the environmental footprint of packaging. Traditional coatings often rely on fossil oil-based polymers. These materials deplete non-renewable resources and contribute to plastic pollution. When you use multilayer films, you encounter recycling challenges. Most recycling facilities cannot separate these layers, so much of this packaging ends up in landfills or incinerators.
- Fossil-based coatings increase global warming potential.
- Biodegradable films, if landfilled, can emit methane—a greenhouse gas far more potent than carbon dioxide.
- Production processes for conventional coatings consume significant energy, especially during drying.
- Some biodegradable coatings may cause higher acidification and eutrophication than petroleum-based films.
- Transport distances and local energy sources also influence the total environmental impact.
Water-based and biodegradable coatings offer a better path. These alternatives break down naturally, reducing plastic waste and microplastic pollution. For example, water-based emulsions and new biopolymer coatings decompose in marine environments, leaving no toxic residues. Marine microorganisms can break down these coatings, turning them into harmless carbon dioxide. You do not need special composting or sewage treatment for disposal. This shift supports a cleaner environment and aligns with global sustainability goals.
🌱 By choosing green coatings, you help reduce landfill waste, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and support a healthier planet.
Benefits of Sustainable Choices
Switching to sustainable coatings brings you more than just environmental benefits. You gain access to new markets as consumers and regulators demand eco-friendly packaging. Companies that adopt green coatings often see improved product shelf life. Enhanced barrier properties protect against moisture, oxygen, and oils, preserving product quality.
- You meet strict environmental regulations, reducing the risk of penalties.
- Your brand reputation improves as you align with sustainability goals.
- Technological advances make sustainable coatings more cost-effective and reliable.
- You differentiate your products in a competitive market.
- Compliance with government policies on plastic waste becomes easier.
Market trends show strong growth for sustainable coatings. The global market is expected to more than double in less than a decade. This growth reflects rising demand and economic incentives for businesses like yours. When you choose sustainable solutions, you not only protect the environment but also strengthen your business position.
💡 Sustainable choices help you future-proof your operations and build trust with customers who value responsible packaging.
Types of Barrier Coating for Paper
Biowax-Based Coatings
You can choose biowax-based coatings when you want to improve water and grease resistance in paper packaging. These coatings use natural waxes, such as carnauba or beeswax, often blended with biopolymers like polylactic acid (PLA). Even at low concentrations, biowax increases hydrophobicity and reduces water absorption. This means your packaging will resist moisture better than uncoated paper.
Biowax-based coatings also enhance grease resistance, making them suitable for food wraps and bakery packaging. When you add PLA, you improve heat sealability and mechanical durability. This combination allows your packaging to withstand converting processes like cutting and folding. Optimized biowax-PLA coatings can match the water resistance of conventional petroleum-based coatings. However, you may notice that grease resistance still falls short of traditional fluorinated or polyethylene coatings, especially under prolonged exposure.
Tip: Use biowax-based coatings for applications where moderate water and grease resistance is needed, and where compostability and renewability are priorities.
Hybrid Coatings
Hybrid barrier coatings for paper combine organic and inorganic materials to deliver superior performance. You often find trimethylsilyl-terminated polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) as a key component. PDMS bonds with cellulose fibers and inorganic fillers, such as platelet-shaped clays, through chemical reactions. This creates a durable, superhydrophobic surface that resists water and air penetration.
You benefit from hybrid coatings when you need enhanced moisture resistance and mechanical strength, especially in wet conditions. These coatings also include blends of fossil-based and bio-based polymers, like starch-acrylic hybrids. Some hybrid solutions use biomimetic approaches, drawing inspiration from plant cuticles. For example, cutin from tomato peels can be processed into waterborne dispersions that provide water, oil, and grease resistance.
Hybrid coatings allow you to balance sustainability with high barrier performance. They work well with standard coating equipment, making them a practical choice for many packaging lines.
Note: Hybrid coatings offer a flexible solution when you need to meet both environmental and technical requirements.
Water-Based Coatings
Water-based coatings represent the fastest-growing segment in the barrier coating for paper market. You see these coatings leading the shift toward sustainable packaging. They use natural materials like starch, cellulose, and calcium carbonate, making them plastic-free, biodegradable, and compostable.
You can rely on water-based coatings to protect food products while minimizing environmental impact. These coatings require less material than polyethylene or PLA coatings to prevent leakage. This efficiency supports your sustainability goals and reduces waste. Water-based coatings also enable coated paper products to be recycled in standard facilities, unlike traditional PE-coated papers that complicate recycling.
Here is a quick overview of the market position for major coating types:
| Coating Type | Market Position / Share / Growth |
|---|---|
|
Water-Based Coatings |
Fastest growing segment with 6.8% CAGR (2025-2035), driven by sustainability and regulatory trends |
|
Paper Coatings |
Dominant material type with 45.3% market share in 2025, favored for recyclability and eco-conscious packaging |
|
Wax Coatings |
Gradually substituted in some applications but remain competitive in low-temperature heat-seal uses |
|
Solvent-Based Coatings |
Niche demand for extreme chemical resistance; growth limited by carbon pricing and insurance costs |
|
Extrusion Coatings |
Mainly LDPE-based; expected to lose market share to dispersion barrier papers in some formats |
You can use water-based coatings for a wide range of applications, from food packaging to compostable paper cups. These coatings are chemically inert and safe for food contact. They do not affect taste or smell. By choosing water-based coatings, you help reduce single-use plastic packaging and promote the reuse of paper fibers.
🌱 Water-based coatings make it easy for you to meet consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging and comply with new regulations.
Biopolymer Coatings
You can choose biopolymer coatings when you want a sustainable and high-performing barrier for paper packaging. Biopolymers such as polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), starch, chitosan, cellulose derivatives, and natural rubber latex come from renewable resources. These materials break down naturally, making them more environmentally friendly than synthetic polymers like polyethylene or polypropylene. When you use biopolymer coatings, you avoid the microplastic pollution and health risks linked to petroleum-based coatings.
Biopolymer coatings provide strong resistance to water, oil, and grease. Starch-based coatings and blends, such as starch with polyvinyl alcohol or chitosan, improve barrier properties while keeping the paper compostable and recyclable. You can safely use these coatings for food packaging because they are non-toxic and derived from natural sources. Although biopolymer coatings may cost more and sometimes offer slightly lower performance than synthetic or PFAS-based coatings, they allow you to claim compostability and recyclability. This aligns your packaging with the sustainability goals that customers and regulators demand.
Tip: If you want to enhance your environmental profile and meet strict green standards, biopolymer coatings offer a reliable solution for barrier coating for paper.
Marine Biodegradable Coatings
You may need marine biodegradable coatings if your packaging could end up in aquatic environments. These coatings break down safely in seawater, reducing the risk of long-term pollution. To ensure true marine biodegradability, you should look for coatings tested under recognized standards. The most relevant standards include EN 13432 for compostability and ASTM D6691, which measures aerobic biodegradation in marine conditions.
Testing for marine biodegradable coatings involves several steps:
- Laboratory reactors simulate composting and marine environments, using methods like ISO 20200 and ISO 14855 to measure disintegration and CO2 evolution.
- Marine pelagic zone simulations suspend coated samples in synthetic seawater to track biodegradation through mass loss or CO2 production.
- Comprehensive test methods expose coatings to different marine habitats, such as sandy beaches, deep sea bottoms, and tidal zones, to assess how they degrade in real-world conditions.
You can trust marine biodegradable coatings to minimize harm if packaging escapes waste streams and enters the ocean. These coatings support your commitment to environmental stewardship and help you meet emerging regulations on marine litter.
🌊 Choose marine biodegradable coatings when you want to protect both land and sea from persistent packaging waste.
Compostable and Recyclable Coatings
You can further boost your sustainability credentials by selecting coatings that are both compostable and recyclable. Compostable coatings break down into harmless substances in industrial or home composting systems. Recyclable coatings allow paper fibers to be recovered and reused, supporting a circular economy.
When you use compostable and recyclable coatings, you avoid the recycling challenges caused by traditional plastic or PFAS-based coatings. Starch-based and other biopolymer coatings make it easier for recycling facilities to process coated paper. You also meet consumer demand for packaging that leaves no trace in the environment.
- Compostable coatings meet standards like EN 13432, ensuring safe breakdown in composting conditions.
- Recyclable coatings allow you to recover high-quality paper fibers, reducing the need for virgin materials.
- Many compostable coatings are also PFAS-free, eliminating harmful chemicals from your packaging.
Note: By choosing compostable and recyclable coatings, you help close the loop on packaging waste and support a cleaner, greener future.
Applying Green Coatings
Green coatings offer you flexible application options, whether you work in a small workshop or a large industrial facility. Understanding the right method and equipment helps you achieve consistent results and meet sustainability goals.
Application Methods
You can choose from several proven techniques to apply eco-friendly coatings to paper. Each method suits different production scales and end-use requirements.
Curtain Coating
Curtain coating creates a continuous, even layer of coating as paper passes under a falling “curtain” of liquid. You benefit from high-speed operation and uniform coverage. This method works well for large-scale production where you need precise control over coat weight. Curtain coating minimizes waste and supports efficient use of green materials.
Spray Coating
Spray coating uses fine nozzles to distribute the coating evenly across the paper surface. You can adjust spray patterns and droplet size to match your needs. This method suits both small batches and specialty applications. Spray coating allows you to target specific areas or apply multiple layers for enhanced barrier properties.
Roll Coating
Roll coating remains one of the most common and versatile methods. You feed paper through rollers that apply the coating in a controlled manner. This technique ensures good adhesion and smoothness. Roll coating adapts easily to different paper types and coating formulations. In industrial settings, you often see rod coating, rotogravure, and flexographic printing as variations of roll-based application. These methods deliver reliable coverage and maintain high runnability on paper substrates.
Tip: Optimize coat weight and number of passes based on your paper’s smoothness and porosity for best results.
Tips for Small Scale
You can apply green coatings on a small scale using equipment that fits your budget and space. Many green coatings work with existing flexographic or standard coating machines, so you do not need to invest in specialized machinery. This compatibility streamlines your transition to sustainable packaging.
| Equipment Component | Description |
|---|---|
|
Loads raw paper for coating |
|
|
Coating Applicator |
Applies coating via roll, air knife, or knife methods |
|
Drying System |
Uses hot air or infrared to dry coated paper |
|
Rewinding Unit |
Rolls finished paper for storage or further use |
|
Coating Flow Control |
Ensures even and accurate coating application |
|
Tension Control |
Prevents wrinkles and misalignment during processing |
|
Inspection System |
Detects surface defects or inconsistencies |
Note: Start with small test runs to fine-tune your process and minimize material waste.
Tips for Industry
You can scale up green coating processes using industrial equipment designed for high throughput and quality. Industrial methods like rod coating, rotogravure, and flexographic printing provide effective coverage and meet regulatory standards for food contact. You should optimize parameters such as coat weight and drying time to match your substrate’s characteristics. Aqueous and UV coatings integrate smoothly with existing production lines, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional films.
- Use automatic control panels and inspection systems to maintain consistency.
- Monitor drying and cooling systems to prevent defects like wrinkles or uneven surfaces.
- Regularly calibrate tension and flow controls for optimal performance.
💡 Industrial adoption of green coatings not only improves your environmental footprint but also enhances product quality and compliance.
Performance and Limitations
Effectiveness
You expect green coatings to perform as well as traditional options. Recent advances have made this possible. Green coatings use materials like cellulose nanofibers (CNF), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and isolated soy protein (ISP) to create dense films. These films fill the gaps between paper fibers, blocking moisture and oil. When you add alkyl ketene dimer (AKD), you boost water repellency by bonding hydrophobic groups to the fiber surface. Scanning electron microscope images show that coated paper has fewer pores than uncoated paper, which explains the improved barrier properties.
Here is a comparison of key performance metrics:
| Coating Type | Key Performance Metrics | Comparison to Traditional Coatings |
|---|---|---|
|
PVA/CNF/MBP/AKD composite coating |
Comparable or better moisture barrier; biodegradable |
|
|
CNF-based coatings |
Oil penetration time > 45 minutes (10 g/m²) |
Better oil resistance than uncoated paper |
|
Isolated Soy Protein (ISP) coating |
Grease resistance up to 2 hours |
Outperforms ordinary polyethylene composite food paper |
|
AKD-CNF coated paper |
Water contact angle up to 113°; moderate oleophobicity (kit 9) |
Good hydrophobicity; oleophobicity still limited |
|
Traditional polyethylene coatings |
Stable, long degradation time, environmental concerns |
Effective barrier but not eco-friendly |
|
Fluorine-containing coatings |
High oleophobicity, health and environmental risks |
Superior oleophobicity but toxic and non-biodegradable |
Note: Green coatings now match or exceed traditional coatings in moisture and grease resistance for many uses. Some limitations remain in extreme oil resistance.
Durability
You need packaging that stands up to real-world handling. Green coatings offer strong durability for most applications. When you use CNF or PVA-based coatings, you get a flexible yet tough surface. These coatings resist cracking and peeling during folding, cutting, and sealing. Biopolymer blends, such as starch with chitosan or PLA, add mechanical strength and heat sealability. You can rely on these coatings for food wraps, cups, and trays that must endure transport and storage.
However, you may notice that some green coatings have lower resistance to prolonged exposure to oils or high humidity compared to fluorinated or polyethylene coatings. For most food packaging and consumer goods, the durability meets industry standards. If you need extreme barrier properties, you may need to combine green coatings with other materials or use hybrid solutions.
💡 For best results, match the coating type to your product’s specific needs and test under real conditions.
Recyclability
You want packaging that fits into existing recycling systems. Green coatings make this possible. Unlike traditional plastic barriers, these coatings allow paper fibers to be reclaimed efficiently. You do not need complex separation or cleaning steps. This means you recover more fiber and reduce waste. Most green coatings use water-based formulas and avoid harmful chemicals like PFAS and VOCs. This keeps the recycling process safe and clean.
When you choose green coatings, you support a circular economy in the paper industry. You help reduce reliance on fossil-based plastics, which are hard to recycle and persist in the environment. Your packaging meets growing regulatory and consumer demands for sustainability.
🌱 Green coatings let you offer recyclable packaging without sacrificing essential barrier properties.
Choosing the Right Solution
Needs Assessment
You need to start by understanding your packaging requirements before selecting a coating. Begin by identifying the type of product you want to protect and the specific challenges it faces. Different products require different barrier properties. For example, food items often need protection from moisture, grease, and oxygen, while industrial goods may require resistance to abrasion or chemicals.
Consider these factors when assessing your needs:
- Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR): Lower MVTR means better moisture protection.
- Cobb Test: Lower Cobb values indicate stronger water resistance.
- Kit Test: Higher kit ratings show better oil and grease resistance.
- Substrate type: Paperboard, corrugated board, kraft paper, and specialty papers each have unique properties.
- Product sensitivity: Evaluate moisture, oxygen, and aroma sensitivity.
- Application method: Ensure compatibility with your current equipment and processes.
- Regulatory compliance: Check for food contact safety and other legal requirements.
- End-use industry: Food, pharmaceuticals, personal care, and industrial sectors have different standards.
Testing methods such as MVTR, Cobb, and Kit tests help you verify if a coating meets your performance needs. Always match the coating to your product’s specific demands.
Sustainability Goals
You should align your coating choice with your company’s sustainability objectives. Many businesses now shift from multi-material laminates to mono-material packaging to support the circular economy. Water-based and water-dispersible coatings help you improve recyclability because they dissolve or disperse during recycling, making fiber recovery easier.
Bio-based and compostable coatings, such as those made from PLA or PHA, reduce reliance on fossil fuels and support composting at the end of life. Heat-sealable coatings compatible with paper allow you to avoid multi-layer plastics, keeping your packaging recyclable. Eliminating hazardous substances like PFAS and chlorinated polymers ensures your packaging remains safe and compliant with regulations.
Consumer demand for sustainable packaging continues to rise, with about 70% of buyers considering sustainability in their purchasing decisions. Regulatory trends, especially in Europe, push for recyclable and compostable coatings. By choosing green coatings, you meet both market and legal expectations.
🌱 Align your coating selection with your sustainability targets to build trust and stay ahead of regulations.
Selection Checklist
You can use a checklist to simplify your decision-making process. This approach ensures you cover all critical aspects before finalizing your choice.
- Design considerations: Assess weight, space, durability, and sustainability.
- Manufacturing considerations: Focus on consistency, repeatability, and cost.
- Operating and use considerations: Address environmental exposures such as moisture, temperature, and handling.
- Market considerations: Ensure compliance with standards and warranty requirements.
- Expected value: Evaluate how the coating reduces risk, controls costs, and adds value to your product.
Tip: Review this checklist with your team to ensure your chosen coating meets both performance and sustainability goals.
Success Stories
Business Adoption
You see many leading companies embracing green coatings to meet sustainability goals and market demands. International Paper Company stands out as a pioneer in this space. The company developed the Bow Tie Shipper, a patented packaging design that reduces material use and eliminates adhesive joints. This approach not only saves resources but also simplifies recycling. International Paper also introduced OHMEGA® Conductive Ink + Touchcode™ technology, which uses eco-friendly conductive ink to add smart features to packaging while supporting environmental responsibility. The company continues to expand its sustainable packaging capabilities by acquiring new facilities and collaborating with partners to lower energy use and carbon emissions in pulp manufacturing.
You also notice a strong industry trend as other major manufacturers adopt green coatings. Companies like Paramelt B.V, Cortec Corporation, Sierra Coating Technologies LLC, Stora Enso Oyj, Michelman Inc., OMNOVA Solutions Inc., Sonoco Products Company, Koninklijke DSM NV, BASF SE, and Dow Chemical Company have all shifted toward biodegradable, recyclable, and water-based coatings. These solutions improve paper’s resistance to moisture and grease without relying on harmful chemicals. Innovations such as nanocoatings and bio-derived barrier agents continue to drive product durability and sustainability across the sector.
🌱 When you follow the lead of these industry giants, you position your business for long-term success and environmental leadership.
Packaging Case Studies
You can measure the impact of green coatings through real-world results. For example, researchers applied electrospun polybutylene succinate coatings to cardboard and saw oxygen transmission rates drop from over 430,000 cm³/m²·day in uncoated samples to as low as 70 cm³/m²·day. This dramatic improvement means your packaging can better protect sensitive products from oxygen exposure.
Another case involved acid-modified polyvinyl alcohol coatings. These coatings achieved an oxygen transmission rate of just 0.13 mL/m²·day and a water vapor transmission rate of 0.82 g/m²·day. Recyclability tests showed a repulpability rate of 99.7%, so you can maintain high recyclability while delivering excellent gas barrier performance.
You also benefit from bio-calcium carbonate coatings, which significantly enhance water resistance. The table below shows the improvements in water contact angle and absorptivity before and after coating:
| Measurable Outcome | Filter Paper (Before) | Filter Paper (After) | Packaging Paper (Before) | Packaging Paper (After) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Water Contact Angle (°) |
Non-measurable |
122 |
109 |
132 |
|
Water Absorptivity (g/m²) (Cobb test) |
150 |
9 |
43 |
7 |
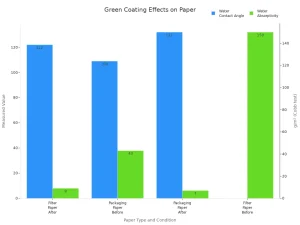
📈 These measurable outcomes show that green coatings can deliver superior protection and recyclability, helping you meet both performance and sustainability targets.
Future Trends
New Materials
You will see a wave of new materials transforming the future of sustainable packaging. Researchers have developed a biodegradable composite by combining lignin nanotubes (LNTs) with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). This LNT/PVA composite delivers strong protection against water vapor, oxygen, and UV light. You can use it for food and medicine packaging because it also provides antimicrobial properties. The hydrogen bonding between lignin and PVA increases mechanical strength and thermal stability. This means your packaging can better withstand handling and storage. The composite reduces water vapor and oxygen transmission rates compared to pure PVA. It also blocks nearly all UV rays and inhibits over 99% of Staphylococcus aureus growth. Both lignin and PVA break down naturally, so you support environmental sustainability with every use.
You will also notice companies like Siegwerk advancing functional barrier coatings. Their focus lies in bridging the gap between plastic and fiber-based solutions. They optimize resistance to water, oxygen, oils, and UV light. These coatings remain compatible with paper recycling processes, so you can maintain a circular economy. The industry continues to push for coatings that meet high performance standards while supporting recyclability and renewability.
🌱 New materials offer you the chance to combine high barrier performance with true environmental responsibility.
Innovation
You benefit from rapid innovation in barrier coatings for paper packaging. The industry now uses bio-based coatings from chitosan, starch, and cellulose. These materials improve sustainability and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Water-based coatings have become popular because they provide moisture resistance without synthetic polymers. You also see a reduction in VOC emissions, which makes your operations safer and more eco-friendly.
Nanocoatings represent another leap forward. They enhance barrier properties at the microscopic level, giving you better protection against moisture and oxygen. Compostable coatings now decompose in both industrial and home composting systems. This reduces environmental impact and meets growing consumer demand for green packaging.
- HyperBarrier, a mineralized ternary nanocomposite, stands out for its performance. It offers a 20-fold improvement in oxygen barrier and a 15-fold boost in moisture barrier compared to polyethylene coatings.
- You can reduce plastic content by 40% with HyperBarrier, while keeping your packaging fully recyclable in existing paper waste streams.
- The coating maintains heat-sealability and food safety, so you do not sacrifice functionality.
- You can use HyperBarrier with your current manufacturing equipment, avoiding extra costs.
Projects like SustaPack and Pulpex Ltd drive further progress. SustaPack develops sustainable liquid packaging with improved barrier coatings. Pulpex produces degradable bottles from natural wood fibers, which you can recycle with regular paper. Multi-layered coatings prevent leaks and oxygen entry, keeping products fresh. New coating processes use less energy and water. Some even use dry spray methods for food-safe, degradable coatings. AI and thermal imaging now help detect and fix coating defects in real time, so you achieve higher quality and less waste.
💡 By embracing these innovations, you stay ahead in sustainability, performance, and operational efficiency.
You now have access to eco-friendly coatings that deliver strong protection and support sustainability goals. Multi-layer coatings using chitosan and starch-based solutions show that green options can match the performance of traditional materials while staying safe and biodegradable.
Switching to green coatings helps you meet regulations, reduce waste, and improve your brand’s image.
Ready to make the change? Explore EPA guides, technical support, and expert webinars to start your journey. Share your experiences or reach out for more guidance.
FAQ
What makes a barrier coating “green”?
You choose a green barrier coating when it uses renewable, biodegradable, or compostable materials. These coatings avoid harmful chemicals like PFAS. They support recycling and reduce environmental impact. You help close the loop on packaging waste by selecting these options.
Can you recycle paper with green barrier coatings?
Yes, you can recycle most papers coated with water-based or biopolymer green coatings. These coatings disperse or break down during standard recycling. Always check local recycling guidelines for best results.
How do you apply barrier coatings to paper?
You can use several methods:
- Roll coating
- Spray coating
- Curtain coating
Choose the method that matches your equipment and production scale. Test small batches first to optimize results.
Are green barrier coatings safe for food contact?
You can trust certified green coatings for direct food contact. Manufacturers test these coatings for safety and compliance with FDA or EU regulations. Always verify certifications before use.
Do green coatings affect print quality?
You achieve excellent print quality with most green coatings. These coatings create a smooth surface that supports vibrant graphics. Some formulations even enhance ink adhesion and color sharpness.
How do green coatings compare to traditional coatings in performance?
You get strong moisture and grease resistance with green coatings. Many match or exceed traditional options for most packaging uses. Some extreme oil or chemical resistance may still require specialty solutions.
What should you consider when choosing a green barrier coating?
Consider these factors:
- Product type and sensitivity
- Required barrier properties
- Compatibility with your equipment
- Regulatory compliance
- End-of-life options (recycling or composting)
Review your needs and sustainability goals before making a selection.






