
Barrier Coating creates a powerful shield that keeps paper both strong and safe. This technology boosts durability and ensures safety by blocking threats like moisture, grease, and harmful contaminants. In everyday products, barrier coatings guard against:
- Moisture infiltration, which can lead to spoilage
- Grease absorption, which affects product quality
- Environmental contaminants such as mineral oils, phthalates, and benzophenones
- External odors and fats
People rely on these coatings to keep packaging fresh, clean, and reliable. Companies use barrier coatings to extend shelf life and reduce waste, making them essential for modern packaging.
Key Takeaways
- Barrier coatings make paper stronger and protect it from moisture, grease, and harmful contaminants, keeping products safe and fresh.
- These coatings improve packaging durability, extend shelf life, and help reduce waste by blocking water, oils, and oxygen.
- Water-based and bio-based barrier coatings support recycling and sustainability, offering eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics.
- Barrier coatings meet strict safety standards, ensuring food and medical packaging stay safe without affecting taste or smell.
- Industries benefit from cost savings, regulatory compliance, and better product protection, while consumers enjoy safer, longer-lasting products.
What is Barrier Coating

Definition
Barrier coating refers to a specialized layer applied to paper products that transforms ordinary paper into a high-performance material. Manufacturers design these coatings to give paper resistance against water, oil, alcohol, and other substances that can weaken or damage packaging. The technology behind barrier coatings offers several advantages:
- Provides strong resistance to water, oil, and alcohol, keeping contents safe from leaks and spills.
- Enhances printability, allowing for vibrant and detailed graphics on packaging.
- Maintains integrity even when exposed to hot or cold water.
- Protects against oils at both low and high temperatures, extending the shelf life of packaged goods.
- Prevents paper layers from sticking together, thanks to superior anti-blocking properties.
- Enables heat-sealing, which creates airtight and moisture-resistant packaging.
- Resists damage from alcohol, ensuring the packaging remains functional.
- Improves bending resistance, so paper can fold without tearing.
- Delivers waterproofing, preserving the strength and appearance of the package.
Purpose
Barrier coating serves a vital role in modern packaging. It protects both the product and the consumer by blocking harmful elements such as light, oxygen, humidity, and microbes. This protection ensures food safety, maintains product quality, and keeps consumers safe. Companies rely on barrier coatings to improve grease resistance, heat tolerance, and peel ability, making packaging more reliable and user-friendly. These coatings also enhance printing and finishing, giving brands the opportunity to stand out on store shelves.
By using barrier coatings, industries can reduce their dependence on plastics, supporting sustainability goals and offering recyclable packaging solutions. The coatings provide a safe alternative to harmful chemicals, delivering grease and moisture resistance without environmental risks. They keep food fresh and flavorful by locking in gases, moisture, and oils, while blocking contaminants that cause spoilage. Barrier coating ensures packaging meets strict safety standards and delivers consistent performance from production to the consumer’s hands.
How It Works
Strength Enhancement
Barrier coating transforms ordinary paper into a robust material ready for demanding applications. Manufacturers often use multilayer cellulose-based coatings, such as microfibrillated cellulose and nanocellulose, to create dense, uniform layers on paper fibers. These layers fill gaps between fibers, reducing porosity and forming a continuous network. Nanofibrillated cellulose bonds with the paper through hydrogen bonding, which increases mechanical strength and durability. Cationic chitosan further reinforces the structure by adhering to the negatively charged cellulose, resulting in a stronger, more resilient paper.
When applied with advanced methods like spray coating, the barrier layer covers the paper evenly, boosting its tensile strength and flexibility. Kraft paper coated with specialized binders can achieve tensile strengths around 53 MPa, maintaining performance even in moist conditions. This improvement means packaging can withstand rough handling, folding, and exposure to liquids without tearing or losing integrity.
Laboratories measure these enhancements using standardized tests. The table below highlights typical results:
| Test Parameter | Method/Equipment | Results Summary |
|---|---|---|
|
Tensile Strength |
Universal testing machine |
Coated papers show 23–25% higher tensile strength than base paper |
|
Elongation at Break |
Universal testing machine |
Coated papers have at least 32% higher elongation at break compared to base paper |
These results prove that barrier coating delivers a significant boost in strength, making paper packaging a reliable choice for both manufacturers and consumers.
Safety Features
Barrier coating does more than strengthen paper—it also protects products and consumers from harmful substances. The coating forms a physical and chemical shield that blocks contaminants like phthalates, mineral oils, and plasticizers from migrating into packaged goods. Manufacturers design these coatings to resist moisture, oxygen, grease, and even flavors, preserving food freshness and safety.
Food packaging made with barrier-coated paper must meet strict international standards. These include uniform thickness, high burst and tear factors, and excellent grease resistance. The coatings often incorporate additives like oxygen scavengers and antimicrobials, which extend shelf life and maintain food quality.
Barrier coatings also comply with FDA regulations. They use approved raw materials and prevent the migration of substances into food. Functional barriers allow the use of certain materials if studies show no migration risk. This approach ensures that packaging remains safe for direct food contact, giving consumers peace of mind.
By combining strength and safety, barrier coating technology sets a new standard for modern packaging. It protects products, supports sustainability, and builds trust with consumers.
Barrier Coating Benefits

Moisture Resistance
Moisture can quickly weaken paper and ruin packaged goods. Barrier coatings create a powerful shield that blocks water and vapor from entering the paper. This protection keeps products dry and safe, even in humid environments. Studies show that paper treated with advanced coatings such as AKD and ASA can reduce the water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) by up to 35% compared to untreated paper. Some multi-component coatings, which include nanocellulose and PVA, achieve a WVTR as low as 100 g/m²/day. Even more impressive, composite films with SiO2@PDA nanoparticles can lower WVTR to just 4.11 g/m²/24 h, making them ideal for packaging moisture-sensitive products.
Moisture resistance is not just about keeping water out. It also means blocking vapor, fatty acids, and other contaminants that can spoil food or damage sensitive items. This level of protection extends shelf life and reduces waste, giving both consumers and businesses more value.
Modern barrier coatings go beyond moisture protection. They offer advanced features like aroma sealing, which locks in freshness and flavor. Many coatings also provide UV resistance, shielding products from sunlight and preventing color fading or nutrient loss. These properties ensure that packaging remains strong, attractive, and effective throughout its use.
Oil and Grease Protection
Oil and grease can easily penetrate untreated paper, causing stains and weakening the material. Barrier coatings solve this problem by forming a dense, protective film on the paper surface. This film blocks oils, fatty acids, and grease, keeping packaging clean and maintaining its appearance. Water-based coatings with acrylic polymers now match the grease resistance of traditional fluorochemicals, but without the health and environmental risks.
The effectiveness of these coatings is clear in industry tests. The table below compares grease resistance for different types of paper:
| Paper Type | Grease Resistance (Kit Number) | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
Untreated base paper |
Low (not specified) |
Hydrophilic and porous, allowing oil and grease penetration |
|
CNC-composite coated paper |
6 |
Coated with cellulose nanocrystals and other components, improved oleophobicity |
|
Cellulose nanofiber/carboxymethyl cellulose coated paperboard |
6 |
Similar improvement in grease resistance |
|
PVA/CNF/MBP/AKD coated paper |
Up to 12 |
Highest grease resistance at low AKD dosage (<0.05%), but oleophobicity decreases at higher AKD doses |
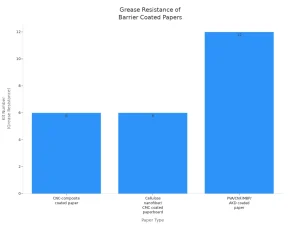
Effective barrier coatings double or even triple the grease resistance of paper. This improvement keeps food packaging looking fresh and appealing, which builds consumer trust and satisfaction.
Advanced coatings also help seal in aromas and flavors, preventing unwanted odors from entering or escaping. Some high-barrier materials, such as aluminum oxide and silicon oxide, block oxygen, moisture, and light, further protecting the contents. These features make barrier coatings essential for packaging snacks, fast food, and other greasy or aromatic products.
Recyclability
Sustainability matters more than ever. Many companies now choose barrier coatings that support recycling and reduce environmental impact. Water-based and bio-based coatings allow paper to remain recyclable and repulpable, unlike traditional polycoated papers that often end up in landfills. For example, Greif’s EnviroRap paperboard uses a water-based coating that makes recycling easier and supports circular economy goals.
Recyclability standards vary by country. The table below shows how much non-paper content is allowed for paper to be considered recyclable:
| Country | Maximum Allowed Non-Paper Content for Recyclability | Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
Germany |
5% |
Paper with more than 5% non-paper content is not recyclable in the waste paper cycle (blue bin). |
|
United Kingdom |
15% (planned reduction to 10%) |
OPRL scheme allows up to 15% external content, with plans to reduce to 10%. |
|
Italy |
Different test method (Aticela 501/19) |
Uses a distinct evaluation method for recyclability. |
Choosing recyclable barrier coatings helps companies meet regulations and consumer expectations. It also reduces waste and conserves resources, making packaging both effective and eco-friendly.
Modern barrier coatings use renewable materials and advanced technology to deliver high performance without sacrificing sustainability. Many coatings now offer repulpability, compostability, and compatibility with existing recycling systems. This progress ensures that packaging protects products and the planet at the same time.
Types of Barrier Coating
Polymer-Based
Polymer-based coatings dominate the packaging industry due to their strong protective properties and versatility. Companies often choose these coatings for food packaging, labels, and cartons. The most common types include polyethylene (PE), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH). Each offers unique advantages for specific applications.
PE coatings set the standard for dry and frozen food packaging, providing reliable moisture barriers. PET, especially when enhanced with nanocoatings, extends shelf life by blocking oxygen and improving flexibility. EVOH coatings excel in paperboard packaging, offering strong oxygen barriers but moderate moisture sensitivity. Starch-based coatings present a biodegradable option, though they remain less effective in humid conditions.
Companies seeking high performance and cost-effectiveness often select polymer-based coatings. However, these coatings can complicate recycling and increase landfill waste, making sustainability a growing concern.
Water-Based
Water-based coatings have surged in popularity as companies prioritize sustainability and regulatory compliance. These coatings use water as the primary solvent, eliminating many harmful chemicals found in traditional polymer-based options.
- Water-based coatings emit no harmful VOCs and dry quickly, reducing environmental pollution.
- They are plastic-free, recyclable with paper, and help cut down on non-recyclable waste.
- These coatings eliminate chemicals like BPA and phthalates, improving consumer health safety.
- Companies adopting water-based coatings align with circular economy principles and meet stricter regulations.
- Water-based coatings are 100% biodegradable and integrate easily into recycling streams.
- Unlike PE-coated paper, water-based coatings do not require labor-intensive separation during recycling.
- Certification programs ensure these coatings remain free from toxins and ozone-depleting compounds.
- Some challenges include the need for specialty additives and higher energy consumption for drying, but ongoing innovation continues to improve their performance and sustainability.
Water-based coatings offer a compelling solution for brands that want to protect products, meet environmental goals, and satisfy consumer demand for greener packaging.
Bio-Based
Bio-based coatings use renewable materials to deliver both protection and environmental benefits. These coatings appeal to companies aiming for compostable, biodegradable, and non-toxic packaging.
| Renewable Material | Description and Use in Barrier Coatings |
|---|---|
|
Polylactic Acid (PLA) |
Biodegradable polymer used for paper packaging barriers. |
|
Polyhydroxy Alkanoates (PHA) |
Biodegradable, suitable for coating paper products. |
|
Starch |
Low-cost, biodegradable; modified starch blends improve moisture resistance. |
|
Chitosan |
Biodegradable; when blended with starch, enhances oil resistance. |
|
Cellulose and Derivatives |
Abundant natural polymer; derivatives like CMC, EC, and HPMC improve coating performance. |
|
Cellulose Nanofibrils (CNF) |
Biodegradable; boosts water and oxygen barrier properties. |
|
Polycaprolactone (PCL) |
Synthetic but biodegradable; improves flexibility and hydrophobicity in blends. |
Bio-based coatings stand out for their low environmental impact. They break down naturally, support composting, and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Companies using these coatings demonstrate leadership in sustainability and respond to growing consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging.
Choosing bio-based coatings helps brands build trust, meet regulatory requirements, and contribute to a cleaner planet.
Uses
Food Packaging
Food packaging relies on advanced coatings to keep products fresh, safe, and appealing. These coatings create a non-reactive shield that blocks contamination and chemical interactions between packaging and food. They protect sensitive items like oils, powders, and juice concentrates, preserving both purity and taste.
- Coatings comply with strict FDA regulations, including CFR 175.300 and 21 CFR Parts 175 and 176, ensuring food safety.
- They provide corrosion resistance and extend the lifespan of packaging during transport and storage.
- Functional barriers prevent migration of substances into food, reducing regulatory burdens for manufacturers.
- Good Manufacturing Practices guarantee coatings do not affect food taste or odor.
Food companies trust these coatings to meet safety standards and deliver products that stay fresh from factory to table.
Medical and Industrial
Healthcare and industry demand packaging that resists moisture, grease, and oil. Coated papers and boards serve as sustainable alternatives to plastic, especially in healthcare packaging and frozen food applications.
- Medical packaging uses these coatings to prevent bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants from penetrating, maintaining product integrity.
- Industrial uses include packaging for seafood, poultry, beef, sugar, flour, and fast food, as well as protective wraps for transport.
- Coatings comply with FDA and BfR standards, making them suitable for direct contact with food and medical devices.
| Application Area | Contamination Prevention Role |
|---|---|
|
Medical Packaging |
Prevents penetration of bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants, maintaining product integrity. |
|
Food Packaging |
Protects against moisture, oxygen, and other contaminants, extending shelf life and maintaining food quality. |
|
Paperboard Packaging |
Enhances strength and durability, protecting products during transport and storage from moisture and contaminants. |
Consumer Products
Everyday products benefit from coatings that boost durability and safety.
| Consumer Product Category | Description / Use Case |
|---|---|
|
Retail Food Containers |
Packaging solutions that enhance durability and safety for retail food items |
|
Trays and Bowls for Microwave and Oven Heating |
Barrier-coated paperboard trays and bowls designed for microwave and oven use |
|
Paperboard Sushi Trays |
Specialized trays for sushi packaging with barrier properties |
|
Paperboard Canisters |
Durable canister packaging made from barrier-coated paperboard |
|
Pouch and Sachet Materials |
Flexible packaging materials including pouches and sachets with barrier coatings |
|
Sterile Medical Barrier Materials |
Protective packaging for medical devices ensuring safety and sterility |
|
Lidding Films |
Films used for sealing trays and containers, tailored for product quality and shelf life |
- These coatings protect products from moisture, oxygen, oils, and dust, preserving freshness and extending shelf life.
- They enhance the durability of paperboard and other substrates, ensuring protection during storage, transport, and use.
- Technological advances, such as water-based and bio-based coatings, offer superior protection without compromising recyclability or adding bulk.
Consumers enjoy longer-lasting, safer products, while manufacturers meet growing demand for sustainable and convenient packaging.
Importance
For Consumers
Consumers gain significant advantages from advanced packaging technologies. Protective coatings on paper packaging keep products fresh, safe, and appealing. These coatings block moisture, oxygen, and UV light, which helps maintain the quality and safety of food, cosmetics, and medicines. Shoppers can trust that their purchases will arrive in excellent condition, even after long journeys or storage.
- Moisture resistance prevents spoilage and keeps products effective.
- Oxygen barriers stop oxidation, preserving freshness, flavor, and color.
- Odor-blocking properties maintain the original scent and prevent contamination.
- UV protection shields nutrients and appearance from light damage.
- Chemical resistance ensures products stay pure and stable.
- Thermal resilience allows packaging to handle temperature changes without losing quality.
- Transparent coatings let consumers inspect products visually, building trust.
Sustainable coatings also matter to today’s shoppers. Many people want packaging that is recyclable, compostable, or made from renewable resources. Eco-friendly coatings help reduce plastic waste and pollution, supporting a cleaner environment. These solutions empower consumers to make choices that align with their values and environmental goals.
Consumers benefit from longer shelf life, reduced waste, and safer products—all while supporting sustainability.
For Industries
Industries experience powerful benefits by adopting modern coating technologies. Companies can extend product shelf life, reduce spoilage, and improve supply chain efficiency. Advanced coatings block moisture, oxygen, and contaminants, which means fewer returns and less product loss.
Manufacturers also save money through operational efficiencies. New binder technologies improve printability and runnability, lowering production costs. Inline application processes allow companies to coat and print in one step, speeding up production and reducing expenses.
Regulatory compliance becomes easier with sustainable coatings. Water-based and bio-based solutions meet strict food safety and environmental standards, including FDA and EPA requirements. These coatings help companies avoid legal risks, meet recycling targets, and enhance brand reputation. As regulations phase out harmful substances and demand greener packaging, industries that innovate with sustainable coatings stay ahead of the curve.
By choosing advanced coatings, industries achieve cost savings, meet regulations, and deliver products that consumers trust.
Barrier Coating delivers unmatched strength and safety for paper in food, medical, and consumer packaging. Recent advances—like compostable and nanocoatings—drive eco-friendly solutions and expand market opportunities. The industry expects rapid growth as demand for sustainable packaging rises, especially in food and healthcare.
Companies and consumers both benefit from reliable, recyclable protection. Ongoing innovation ensures that barrier coatings will shape a greener, safer future for everyday products.
FAQ
What makes barrier coatings better than traditional plastic coatings?
Barrier coatings offer strong protection while supporting recyclability. Companies choose them to reduce plastic waste and meet eco-friendly goals. Consumers benefit from safer, greener packaging.
Choose barrier coatings for a cleaner planet and reliable product safety.
Can barrier-coated paper be recycled?
Yes, most water-based and bio-based barrier coatings allow paper to be recycled easily.
- No need for special separation
- Supports circular economy
- Meets recycling standards in many countries
Are barrier coatings safe for food contact?
Manufacturers use FDA-approved materials in barrier coatings. These coatings prevent harmful substances from reaching food.
Trust barrier-coated packaging for safe, fresh, and high-quality food.
Do barrier coatings affect the taste or smell of packaged products?
Barrier coatings seal in freshness and block external odors. They do not alter the taste or aroma of food.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Aroma sealing |
Preserves flavor |
|
Odor blocking |
Keeps food appealing |
Why should companies switch to sustainable barrier coatings?
Sustainable barrier coatings help companies meet regulations, reduce waste, and attract eco-conscious customers. They also improve brand reputation and support long-term business growth.
Make the switch to lead in sustainability and win customer trust.






