
When you reach for a tissue or paper towel, you expect it to stay strong even when wet. Wet Strength Agents make this possible by reinforcing the fibers and helping the paper resist tearing. You benefit from improved durability and a better user experience every time you use these products. Manufacturers rely on these agents to deliver consistent quality in every sheet.
Key Takeaways
- Wet Strength Agents keep tissue and towel paper strong when wet, preventing tearing and enhancing durability.
- Different types of Wet Strength Agents, both natural and synthetic, offer unique benefits for various applications.
- These agents improve user experience by making paper more absorbent and effective for cleaning tasks.
- Manufacturers can add Wet Strength Agents during production to optimize performance and reduce waste.
- Choosing the right Wet Strength Agent balances strength, softness, and environmental impact for specific needs.
Wet Strength Agents
Definition
You encounter Wet Strength Agents in tissue and towel paper every day. These specialized chemicals help paper maintain its strength when exposed to moisture. When you use a paper towel to clean up a spill, Wet Strength Agents prevent the fibers from breaking apart. Manufacturers add these agents during production to ensure that the paper remains durable and reliable, even in wet conditions.
Types
You find several types of Wet Strength Agents in the tissue and towel paper industry. Each type offers unique benefits for different applications. The most common agents include:
- Polyamideamine Epichlorohydrin (PAE)
- Melamine Formaldehyde
- Polyacrylamide
- Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)
- Modified Starch
- Cationic Polymers (such as polyvinylamine)
You can compare natural and synthetic agents using the table below:
| Type of Agent | Effectiveness | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Natural (e.g., Starch) | Improves strength by forming a film around fibers | More sustainable but less consistent |
| Synthetic (e.g., Polyacrylamide) | Higher strength and performance consistency | Tailored for specific papermaking conditions |
Natural agents like starch offer sustainability, while synthetic agents deliver higher and more consistent performance. You select the right agent based on your product’s requirements and environmental goals.
Role in Paper Products
Wet Strength Agents play a crucial role in the performance of tissue and towel paper. You rely on these agents to keep paper strong and durable when exposed to moisture. They make tissue paper ideal for use in foodservice and medical settings, where wetness is common. Unlike regular tissue paper, which tears or falls apart when wet, products with Wet Strength Agents maintain their integrity. You experience better durability and reliability every time you use these enhanced paper products.
How They Work
Chemical Mechanisms
You rely on Wet Strength Agents to create strong, resilient tissue and towel paper. These agents work through several chemical mechanisms that transform ordinary paper into a product that stands up to moisture. When you add Wet Strength Agents during manufacturing, you trigger a series of reactions:
- Cross-linking occurs between cellulose or hemicellulose fibers and the agent, forming covalent bonds.
- These covalent bonds reinforce the natural hydrogen bonds in the paper, making the structure much stronger.
- The agents create an insoluble network around the fibers, which prevents them from separating when wet.
- Melamine formaldehyde (MF) resin, for example, enhances fiber-fiber bonding through additional covalent bonds and cross-linking, boosting durability in wet conditions.
You can see the main chemical mechanisms in the table below:
| Chemical Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| PAE-resins | Poly Amide-Epichlorohydrine, a common wet strength agent in tissue products. |
| Cationic Resins | Used to achieve desired wet tensile strength. |
| Reactive Groups | Epoxy, amino, hydroxy, or carboxylic groups interact with cellulose fibers. |
| Curing Process | Crosslinking and network formation enhance wet strength. |
| Radical Formation | Increases reactive sites and bonds, further strengthening the material. |
These chemical reactions ensure that your tissue and towel paper do not fall apart when exposed to water.
Fiber Bonding
You benefit from the microscopic changes Wet Strength Agents create within the paper. At the fiber level, these agents alter the way fibers connect and interact. Two main mechanisms come into play:
| Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Protection Mechanism | The agent distributes onto the fiber, diffuses into the fiber wall, and forms an insoluble network. This network impedes fiber wetting and preserves dry strength even after rewetting. |
| Reinforcement Mechanism | The agent reacts with cellulose, forming covalent bonds between molecules and fibers. This process reinforces natural hydrogen bonding and maintains strength in wet conditions. |
For example, when you use a crosslinking agent like butanetetracarboxylic acid (BTCA) with sodium hypophosphite as a catalyst, you get esterification. This reaction forms strong bonds between the agent and cellulose, resulting in a network that resists water and keeps the paper intact.
Impact on Wet and Dry Strength
You notice the difference Wet Strength Agents make every time you use a tissue or towel. These agents do more than just keep paper strong when wet. They also help maintain dry strength, so the product performs well in all conditions.
When you add Wet Strength Agents, you create a paper that resists tearing, holds together during use, and delivers a reliable experience whether wet or dry.
You can trust that the paper will not disintegrate during cleaning or wiping. The combination of chemical cross-linking and enhanced fiber bonding ensures that both wet and dry strength remain high. This balance is essential for products used in kitchens, bathrooms, and healthcare settings, where durability and reliability matter most.
Benefits
Durability
You expect tissue and towel paper to stay strong during use, especially when wet. Wet Strength Agents reinforce the paper fibers, making each sheet more resistant to tearing and disintegration. You notice this durability when you clean up spills or wipe surfaces. The paper maintains its structure, even after absorbing moisture. Manufacturers design these products to withstand repeated handling, so you can rely on them for tough cleaning tasks. This increased durability means fewer sheets are needed, reducing waste and improving efficiency in homes and businesses.
User Experience
You want tissue and towel paper that feels soft, absorbs quickly, and performs well. Wet Strength Agents help deliver these qualities. Surfactants, used as rewetting agents, can reduce water absorbency time and improve the hydrophilicity of fibers. This makes the paper more effective and pleasant to use. Studies show that surfactants enhance absorbency in both high-quality and lower-quality products. You benefit from faster cleanups and a more comfortable touch. The table below highlights how surfactants improve user experience:
| Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Surfactants as Rewetting Agents | Surfactants reduce water absorbency time and improve fiber hydrophilicity. |
| Impact on Absorbency | Surfactants increase absorbent properties, making products more effective. |
| Research Objectives | Studies evaluate surfactant performance and optimal application methods. |
You experience better results with every use, whether you need a quick wipe or a gentle tissue.
Versatility
You use tissue and towel paper in many settings, from kitchens to hospitals. Wet Strength Agents make these products versatile by allowing them to perform well in different environments. The table below shows how these agents expand the range of applications:
| Application | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Cleaning | Maintains integrity when wet, essential for effective cleaning. |
| Packaging | Provides durability and moisture resistance for packaging materials. |
| Medical Uses | Ensures hygiene and reliability in medical applications. |
You find wet strength paper in paper towels, napkins, and medical supplies. These products withstand moisture, making them suitable for cleaning, food service, and healthcare. You can trust their performance in any situation.
Manufacturing

Application Process
You encounter two main methods for adding Wet Strength Agents during papermaking. Manufacturers can introduce these agents directly into the initial pulp mixture or apply them in a separate treatment step after preparing the pulp. The table below outlines these methods:
| Method of Addition | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Pulp Mixture | Wet strength agents are added directly to the pulp at the beginning of the process. |
| Separate Treatment Step | Agents can also be applied in a subsequent step after the initial pulp preparation. |
You may see both natural and synthetic agents used in these processes. For example, starch and chitosan represent natural options, while PAAE and PEI are common synthetic choices. Chitosan stands out for its biocompatibility and ability to form thicker, tunable coatings. It also offers environmental safety and economic benefits compared to some synthetic agents.
- Chitosan creates more pronounced film properties than synthetic agents.
- Its biocompatibility is important for safety and sustainability.
- Chitosan can be combined with other materials for specialized applications.
Production Efficiency
You benefit from improved production efficiency when manufacturers use advanced wet strength resins. For instance, FennoStrength resins have shown a 10 to 15% increase in efficiency over standard resins. In some cases, you see a 25% reduction in chemical dosage and a 28% decrease in energy consumption, which leads to over 10% net cost savings. By balancing fiber charges, these agents help optimize the papermaking process and reduce waste.
Quality Control
You rely on strict quality control measures to ensure the effectiveness of wet strength treatments. Manufacturers use real-time monitoring of chemical additives to maintain product quality. Zeta potential analysis helps track the retention of fines, fillers, and dyes, which is crucial for achieving the desired paper properties. Devices like the emtec FPO provide online measurements, allowing for immediate adjustments during production. The table below summarizes key quality control practices:
| Quality Control Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-time monitoring of chemical additives | Determines optimal additive quantities and maintains consistent product quality. |
| Zeta potential analysis | Offers insights into retention of fines, fillers, and dyes for quality assurance. |
| Testing devices (e.g., emtec FPO) | Provides real-time data to optimize production before laboratory testing. |
These steps ensure that you receive durable, high-performing tissue and towel paper every time.
Performance Comparison

With Wet Strength Agents
When you use tissue and towel paper enhanced with Wet Strength Agents, you notice a clear difference in performance. These products maintain their structure and resist tearing, even after absorbing water. You can see this in the numbers:
| Product | Dry Tensile Strength (gf/in) | Wet Tensile Strength (gf/in) |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional paper towels – hard wound | 1000 – 3100 | 250 – 850 |
| Institutional paper towels – center pull | 400 – 1500 | 100 – 500 |
| General-purpose wipers | 800 – 2700 | 230 – 600 |
| Retail paper towels – folded | 800 – 2700 | 230 – 600 |
You experience this strength every time you use a kitchen towel that does not fall apart during tough cleaning. Napkins and food packaging also benefit from these agents, especially in Europe, where kitchen towels use advanced G 2 and G2.5 agents for higher tolerance. Food packaging and filter papers require G 3 agents to ensure durability and moisture resistance. Many manufacturers now use bio-based agents from renewable materials like starches and polysaccharides, which support eco-friendly choices.
Without Wet Strength Agents
If you use tissue or towel paper without these agents, you quickly notice the difference. The paper loses strength when wet and tears easily. You may need to use more sheets to complete a simple task, which increases waste and frustration. Products without these agents cannot meet the demands of food service, medical, or packaging applications. They often fail in wet conditions, making them unsuitable for many real-world uses.
You depend on the right balance of strength and absorbency. Wet Strength Agents make that possible, giving you reliable performance in every sheet.
Considerations
Usage
You need to consider how much wet strength your tissue or towel paper requires. Products for kitchens, hospitals, or food service demand higher wet strength to handle spills and repeated use. However, not every application benefits from maximum wet strength. If you choose a product for facial tissues or napkins, you may prefer a softer, more absorbent sheet. Manufacturers often adjust the type and amount of wet strength agent to match the intended use. You should look for product labels or specifications that indicate the right balance for your needs.
Trade-Offs
When you increase wet strength, you often see changes in other important properties. You might notice that the paper feels less soft or absorbs less liquid. This happens because the chemicals that boost strength can make the fibers stiffer and less able to take in water. The table below shows how these properties change:
| Property | Effect of Increased Wet Strength | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|
| Softness | Decreased | 24% |
| Absorbency | Decreased | 12% |
| Capillary Rise | Decreased | 42% |
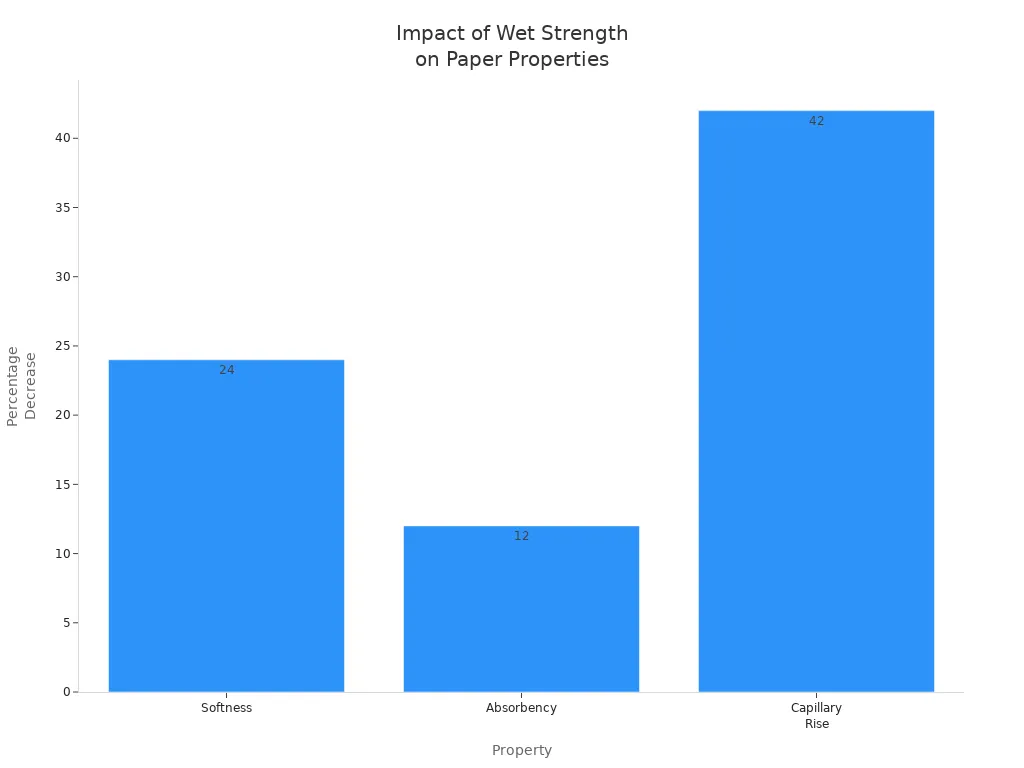
You see that as wet strength rises, softness drops by 24%, absorbency by 12%, and capillary rise by 42%. The use of polymeric additives and dry strength agents can make tissue paper stronger, but you trade off some comfort and absorbency. You should weigh these factors when selecting products for specific tasks.
Environmental Impact
You play a role in supporting sustainability by understanding the environmental effects of wet strength agents. Natural additives like starch or chitosan break down quickly, while synthetic agents can persist in the environment and complicate recycling. The table below compares key impacts:
| Environmental Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Biodegradability | Natural wet strength additives break down quickly, while synthetic ones can persist in the environment, contributing to pollution. |
| Recycling Challenges | Wet strength additives complicate recycling processes, requiring more energy and water, and reducing recycling rates. |
| Resource Consumption | The production of wet strength tissue paper demands significant water and energy, impacting natural resources and contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. |
- Chemicals from wet strength tissue paper can leach into waterways and soil, causing pollution.
- The production of these chemicals can contribute to air pollution.
You also see a positive shift as more manufacturers use bio-based fillers and adhesives. These alternatives lower greenhouse gas emissions and energy use, and they support a circular economy. Adhesives from vegetable oils, for example, biodegrade over months to years and reduce the overall environmental footprint by 22% compared to petrochemical options. By choosing products with eco-friendly agents, you help reduce waste and promote a healthier planet.
You see wet strength agents drive durability, user satisfaction, and efficient manufacturing in tissue and towel paper. Manufacturers report a 42% increase in wet strength and enhanced productivity:
| Metric | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Breaking Length | 32% |
| Wet Strength | 42% |
| Reduction in Paper Breaks | Significant |
| Machine Runability | Improved |
| Productivity | Enhanced |
Understanding these agents benefits you and producers by ensuring reliable products for cleaning and wiping. 🌱 Innovations in bio-based and biodegradable agents continue to improve quality, meet environmental standards, and support future sustainability.
FAQ
What are wet strength agents, and why do you need them in tissue paper?
Wet strength agents are chemicals that help tissue paper stay strong when wet. You need them to prevent tearing and disintegration during use. These agents make products more reliable for cleaning, wiping, and personal care.
Can you recycle tissue paper with wet strength agents?
You may find recycling more difficult with wet strength tissue paper. The agents make fibers resistant to water, which complicates the recycling process. Some facilities use special treatments, but most wet strength paper ends up as waste.
Are wet strength agents safe for you and your family?
Manufacturers test wet strength agents for safety. You can trust that reputable brands follow strict regulations. Most agents do not pose health risks during normal use. Always check product labels for certifications and safety information.
Do wet strength agents affect the softness of tissue paper?
You may notice a slight decrease in softness when wet strength agents are present. These chemicals reinforce fibers, which can make the paper feel firmer. Manufacturers balance strength and comfort to meet your needs.






