
Imagine a shipping box that resists water damage during a rainy delivery or a magazine page that displays crisp, vibrant images without smudging. Surface sizing agents make these outcomes possible by transforming the paper’s surface properties.
-
They reduce absorption, allowing inks and paints to remain on the surface and improving print clarity.
-
These agents enhance water resistance and mechanical strength, increasing durability for packaging and specialty papers.
-
The packaging industry relies on them for high-quality, resilient materials.
Key Takeaways
-
Surface sizing agents improve paper by making it stronger, water-resistant, and better for printing.
-
They form a protective film on paper that keeps ink sharp and prevents water damage.
-
Different regions and industries need specific surface sizing agents to meet local demands and regulations.
-
Starch-based, polymeric, and anionic agents each offer unique benefits and suit different paper uses.
-
Applying surface sizing agents properly requires careful control of coating methods and process conditions.
-
Eco-friendly and bio-based sizing agents are growing in demand due to environmental regulations and consumer preferences.
-
Challenges like coating defects, foaming, and balancing cost with performance require skilled management.
-
Innovations in sustainable and hybrid sizing agents help improve paper quality while reducing environmental impact.
Importance
Paper Quality
Surface sizing agents play a vital role in enhancing paper quality. After the paper sheet forms and partially dries, these agents are applied to the surface. They create a smooth, even layer that cements fibers together, improving both surface strength and bending stiffness. This process results in a paper surface that resists tearing and folding, which is essential for packaging and specialty papers. By forming a film on the surface, these agents also provide a barrier against liquid penetration. This barrier improves water resistance and prevents ink from soaking into the fibers, leading to sharper, more vibrant prints. The use of modified starches, cationic additives, and copolymers further boosts mechanical properties and print quality, although these enhancements may increase production costs.
Note: Evaluation tests such as Cobb, Stöckigt, and Hercules help manufacturers measure how well the paper resists water and ink penetration, ensuring that the final product meets strict quality standards.
Industry Needs
The papermaking industry faces diverse and evolving requirements across global markets. Each region and segment demands specific performance characteristics from surface sizing agents:
-
Asia-Pacific: Focuses on cost-efficient starch-based and synthetic agents for high-speed packaging production.
-
North America: Prioritizes moisture resistance for recycled grades, especially in e-commerce and food packaging, with a push for bio-based solutions.
-
Europe: Balances lightweight packaging and graphic papers, with regulations driving higher water resistance in single-use products.
-
Latin America: Requires wet strength for export packaging and softness for tissue papers.
-
Japan & South Korea: Demands precise control of porosity and thermal stability, with strict safety standards for food packaging.
-
Environmental Regulations: Global mandates limit VOCs and persistent chemicals, encouraging the use of biodegradable and low-impact chemistries.
|
Key Needs |
|
|---|---|
|
Packaging & Board |
Water and abrasion resistance, durability |
|
Printing & Writing |
Printability, compatibility with recycled fibers |
|
Specialty Papers & Tissue |
High purity, biodegradability |
|
Regulatory Compliance |
Environmental safety, low-VOC formulations |
|
Manufacturing Process |
Consistent quality, high-volume production |
|
Supply Chain & Cost |
Cost-performance balance, hybrid agent adoption |
End-User Demands
End-users drive the continuous improvement of surface sizing agents through their expectations for paper performance and sustainability. They seek:
-
Enhanced printability and color vibrancy for magazines, books, and packaging.
-
Superior water and grease resistance, especially for food packaging and shipping materials.
-
Increased mechanical strength to prevent tearing and folding during use.
-
Compliance with environmental standards, favoring bio-based and eco-friendly agents.
-
Functional properties like moisture and grease barriers for specialty applications.
-
Cost-effective solutions that reduce waste and energy consumption.
-
Tailored formulations to match local raw materials and production needs.
The rise of e-commerce and the demand for sustainable packaging have amplified the need for advanced surface sizing agents. Manufacturers must adapt quickly to meet these evolving requirements, ensuring that paper products remain reliable, safe, and environmentally responsible.
Surface Sizing Agents

Definition
Surface sizing agents are specialized chemicals applied to the surface of paper after the sheet forms but before it dries completely. These agents modify the paper’s surface properties, making it stronger, less porous, and more resistant to water and ink penetration. Manufacturers often use starch-based compounds, synthetic polymers, or blends of both. The main goal is to enhance the paper’s performance in printing, packaging, and specialty applications. Surface sizing agents help paper meet industry standards for strength, printability, and durability.
How They Work
Surface sizing agents interact with paper fibers through several mechanisms:
-
They form a thin film on the paper surface, increasing surface strength and stiffness.
-
This film reduces surface porosity, which decreases water absorption.
-
Hydrophobic polymeric nanoparticles, often with a styrene-acrylate core, combine with starch or synthetic polymers in the sizing mixture.
-
The process involves physical adsorption and film formation on the fiber surface.
-
The effectiveness depends on particle charge (cationic, anionic, amphoteric), starch type and concentration, ionic strength, and drying temperature.
-
Cationic particles usually provide better hydrophobization than anionic particles.
-
The application occurs at the dry-end of the paper machine, where the particle-starch mixture coats the paper surface.
-
These combined actions lead to improved printability and reduced water uptake.
Tip: The right combination of starch and polymeric nanoparticles can significantly boost both print quality and water resistance.
Internal vs. Surface Sizing
Internal sizing and surface sizing differ in both their application methods and their effects on paper properties. Internal sizing involves adding agents such as alkyl ketene dimer (AKD), alkenyl succinic anhydride (ASA), or rosin directly into the pulp before the paper forms. This approach enhances hydrophobicity throughout the fiber matrix, affecting the bulk properties of the paper. Internal sizing is essential for improving water resistance and retention across the entire sheet.
Surface sizing, in contrast, targets the paper’s exterior. Manufacturers apply chemicals like starch derivatives, styrene acrylic emulsions, or proprietary treatments onto the surface after the sheet forms. This method improves surface-specific properties such as strength, adhesion, printability, and porosity. Surface sizing allows for more precise control and less chemical waste. It is especially useful for recycled linerboard and printing papers that require enhanced ink performance.
The manufacturing processes also differ. Internal sizing integrates into the wet end of the paper machine, while surface sizing takes place in a separate coating or size press step. Enzymatic modification of starch, such as using β-amylase or pullulanase, can further optimize surface sizing agents for better strength and lower viscosity. This distinction ensures that each method addresses specific performance needs in modern papermaking.
Benefits
Printability
Surface sizing agents play a crucial role in improving the printability of paper. They modify the surface chemistry and physical structure, which leads to better ink interaction and sharper images. When manufacturers apply these agents, the paper surface becomes less absorbent. This change allows ink to remain on the surface, resulting in vibrant colors and crisp text.
Ink Holdout
Ink holdout refers to the paper’s ability to prevent ink from soaking into the fibers. High ink holdout ensures that printed images and text appear sharp and clear. Papers treated with advanced terpolymer-based surface sizing agents show lower Cobb values, which means they absorb less water. This improvement directly enhances ink retention and print sharpness. Contact angle measurements on these papers reveal increased hydrophobicity, confirming that the surface resists ink penetration. Synthetic sizing agents also raise black ink optical density above 2 and yellow ink optical density above 0.9, both considered excellent for print quality. The color gamut area expands, allowing the paper to reproduce a wider range of colors. These quantitative improvements demonstrate that surface sizing agents significantly boost print quality by controlling surface wettability and absorption.
Reduced Picking
Picking occurs when the paper surface lifts or tears during high-speed printing, causing defects and machine downtime. Surface sizing agents strengthen the bond between fibers at the surface, reducing the risk of picking. A well-sized paper maintains its integrity under the mechanical stress of printing presses. This improvement leads to fewer interruptions, higher productivity, and better finished products. Printers can run at higher speeds without sacrificing quality, which is essential for commercial printing operations.
Water Resistance
Water resistance is a key benefit for many paper applications, especially packaging and labels. Surface sizing agents create a protective barrier that repels water and other liquids. This barrier helps maintain the paper’s strength and appearance even in humid or wet conditions.
Liquid Barrier
Surface sizing agents form a thin film on the paper surface, which acts as a liquid barrier. Hydrophobic copolymers applied at the size press increase the water contact angle, making the surface more water-repellent. Unlike internal sizing, these agents do not require chemical curing, so the hydrophobic effect remains stable over time. This treatment proves especially effective for heavier grades of paper, such as corrugated board and carton stock.
|
Aspect |
Explanation / Evidence |
|---|---|
|
Mechanism of Surface Sizing Agents |
Amphiphilic molecules align with hydrophilic ends facing the fibers and hydrophobic ends facing outward, forming a film that reduces surface tension and creates a water-repellent surface. |
|
Measurement Metrics |
Water resistance is measured by Cobb value (water absorption) and dynamic contact angle (wetting behavior). |
|
Interpretation of Metrics |
Lower Cobb values mean less water absorption and better resistance. Higher contact angles (>90°) indicate superior repellency. |
|
Experimental Evidence |
Sized corrugated paper shows a Cobb value drop from 127 g/m² to 22 g/m². Contact angles remain high (e.g., 126.6° at 120 s), indicating sustained water repellency. Unsized papers show lower angles and more water spreading. |
Wetting Resistance
Wetting resistance describes the paper’s ability to resist the spread of water or other liquids across its surface. Surface sizing agents increase the contact angle of water droplets, which means water beads up instead of soaking in. This property is vital for packaging, food wraps, and labels that must withstand exposure to moisture. Papers with high wetting resistance maintain their appearance and performance, even in challenging environments.
Note: High wetting resistance not only protects the paper but also preserves print quality by preventing ink bleed and smudging.
Durability
Durability ensures that paper products can withstand handling, folding, and mechanical stress without losing their integrity. Surface sizing agents enhance durability by reinforcing the fiber network and improving surface strength.
Surface Strength
Surface strength refers to the paper’s ability to resist abrasion, scuffing, and surface damage. When manufacturers use polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) combined with waterborne blocked polyurethane (TBPU) as surface sizing agents, they create a highly crosslinked polymer network. This network forms strong covalent and hydrogen bonds with the paper fibers, filling gaps and reducing porosity. As a result, the paper surface becomes smoother and more resistant to mechanical wear. Improved surface strength also supports better ink adhesion, which is critical for high-quality printing.
Tear and Fold Resistance
Tear and fold resistance are essential for packaging, books, and other products that undergo frequent handling. The TBPU/PVA composite sizing system increases the dry tensile index by 55% compared to untreated paper. Folding resistance improves dramatically, reaching approximately 4453 seconds in laboratory tests. The dense, interpenetrating network formed by these agents reinforces the paper structure, making it less likely to tear or break during use. Polyurethanes add flexibility and abrasion resistance, ensuring that the paper remains strong without becoming brittle. This combination of properties extends the lifespan of paper products and reduces waste.
Optical Properties
Paper’s optical properties play a crucial role in its visual appeal and functionality. High brightness and whiteness levels make printed images and text stand out, which is essential for packaging, publishing, and specialty papers. Manufacturers focus on these properties to meet industry standards and customer expectations.
Brightness
Brightness measures the amount of blue light reflected from the paper surface. High brightness ensures that printed colors appear vivid and true to their original design. Coatings containing ground calcium carbonate (GCC) and starch significantly improve brightness. GCC acts as a filler mineral, scattering light and creating a more reflective surface. Starch binds the filler particles, helping them stay evenly distributed across the paper. This combination increases the paper’s ability to reflect light, resulting in a brighter appearance.
Spectrophotometric measurements, following ISO 2470-1, confirm these improvements. For example, a coating suspension with 15% GCC and 10% starch solids, plus a dispersant, increased brightness by 6.8%. This measurable enhancement demonstrates the effectiveness of mineral fillers and binders in boosting optical performance. Manufacturers rely on these results to ensure their products meet the demands of high-quality printing and packaging.
Note: Brightness is not only about appearance. It also affects readability and the overall perception of quality in printed materials.
Whiteness
Whiteness refers to the paper’s ability to reflect all wavelengths of visible light evenly, giving it a neutral, clean look. High whiteness levels help printed colors remain accurate and prevent unwanted color shifts. The use of GCC in surface coatings creates a white, opaque layer that enhances the paper’s visual appeal. Starch, as a binder, supports the retention of these mineral fillers, although it may slightly increase yellowness if not properly balanced.
Dispersants play a key role by ensuring a homogeneous suspension of coating materials. This even distribution leads to consistent whiteness across the paper surface. According to ISO 11475, papers treated with optimized coatings achieve the highest whiteness levels. These improvements are especially important for graphic papers, magazines, and packaging that require a premium look.
|
Optical Property |
Enhancement Method |
Measurement Standard |
Improvement Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Brightness |
GCC + starch + dispersant |
ISO 2470-1 |
+6.8% brightness with optimized mix |
|
Whiteness |
GCC + starch + dispersant |
ISO 11475 |
Highest whiteness achieved |
Manufacturers continue to refine their formulations to balance brightness and whiteness, ensuring that paper products meet both aesthetic and functional requirements.
Types
Starch-Based
Starch-based surface sizing agents dominate the global papermaking market. Manufacturers prefer these agents for their natural origin, eco-friendly profile, and cost-effectiveness. Starch and its derivatives, such as carboxymethyl cellulose and hydroxyethyl cellulose, improve paper printability, strength, and dimensional stability. These agents work best in acidic paper formulations and remain the primary choice in regions like Asia-Pacific, where the paper and textile industries continue to expand rapidly.
However, starch’s hydrophilic nature presents challenges. When blended with hydrophobic synthetic polymers, starch often shows poor compatibility. This incompatibility leads to weak adhesion and reduced tensile strength in the final paper product. Native starch also suffers from water sensitivity, which limits its use in applications requiring high water resistance. Modifications to starch or the addition of compatible polymers can address some of these issues, but the need for improvement remains.
Tip: Starch-based agents offer a sustainable solution for many paper grades, but their performance may require enhancement for demanding packaging or specialty applications.
|
Type of Sizing Agent |
Examples |
Market Prevalence and Growth |
Regional Market Share |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Natural Sizing Agents |
Starch, Starch Derivatives, Carboxymethyl Cellulose, Methyl Cellulose, Hydroxyethyl Cellulose, Chitosan, Acryloyl Compounds |
Dominant segment due to eco-friendly properties; leading the market with a CAGR of 5.4% |
Widely used globally, especially in Asia-Pacific due to expanding paper and textile industries |
Polymeric
Polymeric surface sizing agents include synthetic compounds such as polyvinyl alcohols, polyacrylates, and modified polyesters. These agents possess amphiphilic properties, with hydrophilic ends that adhere to paper fibers and hydrophobic ends that face outward. This molecular arrangement forms a smooth, water-repellent film on the paper surface. As a result, polymeric agents significantly enhance surface strength, printability, and water resistance.
Acrylate copolymers, for example, improve the durability of both coated and uncoated papers. Polymeric agents also increase ring crush strength in corrugated packaging, making them ideal for high-performance applications. Their compatibility with a wide range of pigments and their ability to cross-link with starch allow for reduced dosage and improved efficiency.
|
Property/Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Forms strong films on paper surfaces, enhancing durability |
|
|
Water Resistance |
Improves water repellency and resistance to moisture |
|
Surface Strength |
Increases surface strength, reducing tearing and breaking |
|
Printability |
Enhances smoothness and print quality |
|
Cross-linking |
Improves cross-linking strength with starch, reducing dosage needed |
|
Packaging Strength |
Increases ring crush strength in corrugated board packaging |
|
Amphiphilic Nature |
Creates a smooth, water-repellent finish |
|
Application Scope |
Used in books, magazines, packaging, writing, and printing papers |
Polymeric sizing agents remain essential for producing high-quality, durable, and water-resistant paper products. Their use continues to grow, especially in regions with strict performance and durability requirements.
Anionic
Anionic surface sizing agents differ from other types in both performance and application. These agents respond positively to the presence of salts like sodium chloride or calcium chloride. Salt addition reduces water uptake by screening charges and improving particle retention on the paper surface. This effect enhances hydrophobization, making the paper more water-resistant.
Anionic agents generally require higher dosages than cationic agents and show greater sensitivity to paper grade. Fine papers, for example, need more anionic sizing agent to achieve the desired effect. However, chemical modifications, such as the addition of organosilicon compounds, can boost their performance. Modified anionic agents increase water resistance, surface gloss, and mechanical strength. Papers treated with these agents show higher contact angles and lower Cobb values, indicating superior liquid repellency.
|
Aspect |
Anionic Surface Sizing Agents |
Cationic Surface Sizing Agents |
|---|---|---|
|
Salt improves hydrophobization and particle retention |
Salt increases water uptake, reduces efficiency |
|
|
Surface Sizing Performance |
Lower, requires higher dosage, sensitive to paper grade |
Superior, less sensitive to paper type |
|
Sensitivity to Paper Type |
High |
Low |
|
Mechanism |
Charge screening by salt enhances retention |
Flocculation by salt reduces effectiveness |
|
Mechanical Strength |
Improved with chemical modification |
Not specified |
Anionic surface sizing agents offer promising results when properly formulated, especially for applications demanding high water resistance and mechanical reinforcement.
Comparison
Selecting the right surface sizing agent depends on the desired paper properties, production requirements, and end-use applications. Each type—starch-based, polymeric, and anionic—offers unique advantages and limitations.
|
Sizing Agent Type |
Strengths |
Weaknesses |
Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Starch-Based |
Renewable, cost-effective, good printability |
Limited water resistance, compatibility issues with hydrophobic polymers |
General printing, eco-friendly packaging |
|
Polymeric |
Superior water resistance, high durability, customizable |
Higher cost, synthetic origin |
High-performance packaging, specialty papers |
|
Anionic |
Enhanced water repellency with salt, improved mechanical strength with modification |
Higher dosage needed, sensitive to paper grade |
Specialty papers, applications needing high liquid resistance |
Researchers have compared these agents in various studies. For example, blending oxidized starch with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) improves both mechanical and surface properties. The combination increases breaking length and burst index, while also enhancing gloss and reducing air permeance. PVA’s film-forming ability reduces porosity and strengthens the paper surface, making the blend more effective than oxidized starch alone.
Another study compared a conventional polyDADMAC-based sizing agent with an environmentally friendly cationised starch alternative. Cationised starch produced sharper prints and higher ink density by limiting ink penetration. However, it also led to longer ink setting times and mottling, especially with cyan ink. These drawbacks can limit its use in fast-paced industrial settings. The study also explored concerns about polyDADMAC’s impact on recyclability but found no negative effects.
Surface chemistry plays a crucial role in print quality. Research shows that blends of cationic starch and styrene copolymers can tailor the surface energy of paper, directly affecting inkjet print performance. By adjusting the ratio of these polymers, manufacturers can optimize contact angle and surface structure, leading to better ink holdout and sharper images.
Coating composition also matters. Papers coated with silica pigments show improved ink wetting, broader color gamut, and sharper prints. Polyvinyl alcohol enhances color range but may reduce print sharpness compared to cationic starch. These findings highlight the importance of matching the sizing agent and coating formulation to the specific needs of the paper grade and printing process.
Tip: Manufacturers often use blends of natural and synthetic agents to balance cost, performance, and sustainability. The right combination can deliver superior print quality, durability, and environmental compliance.
Application

Size Press
The size press stands as the most widely used method for applying surface sizing agents in modern papermaking. This equipment applies a thin, even layer of sizing solution to both sides of the paper sheet after formation but before final drying. The process improves surface strength, water resistance, and printability. Manufacturers often choose the size press because it delivers consistent results and adapts to various paper grades.
Film Press
The film press represents an advanced evolution in size press technology. It uses metering rolls to apply a controlled, uniform film of sizing agent onto the paper surface. This method allows precise adjustment of application rates, which leads to better control over paper properties. The film press reduces operational issues such as sheet edge defects and uneven profiles. It also minimizes drying demands and sheet breaks, resulting in higher efficiency and stable production. Modern film presses, like the IntelliSizer and OptiSizer Curtain, can operate at speeds up to 1700 meters per minute. These systems maintain flexibility for different product requirements and consistently deliver high-quality paper with enhanced surface strength and water resistance.
Pond Press
The pond press, a traditional size press design, creates a pond of sizing solution between two rolls. The paper passes through this pond, absorbing the sizing agent. While effective, the pond press can suffer from turbulence and poor pickup control. These issues may lead to uneven application and increased drying needs. Despite these challenges, the pond press remains in use for certain grades where high penetration is desired. However, many mills now prefer film presses for their superior control and efficiency.
Coating Methods
Surface sizing agents can also be applied using various coating methods. These techniques include blade coating, rod coating, and curtain coating. Each method offers unique advantages:
-
Blade coating uses a flexible blade to spread the sizing agent evenly across the paper surface, producing a smooth finish.
-
Rod coating employs a wire-wound rod to meter the sizing solution, allowing for precise thickness control.
-
Curtain coating creates a continuous curtain of sizing agent that falls onto the moving paper, ensuring uniform coverage even at high speeds.
These coating methods enable manufacturers to tailor the surface properties of paper for specific end uses. They also support the use of advanced sizing agents, such as waterborne polyurethanes and synthetic polymers, which enhance water resistance and mechanical strength.
Tip: Selecting the right coating method depends on the desired paper properties, production speed, and compatibility with different sizing agents.
Process Factors
Several process factors influence the effectiveness of surface sizing application:
-
Viscosity of the sizing solution affects penetration and film formation.
-
Temperature and drying rate impact the final surface strength and water resistance.
-
Paper speed and tension determine the uniformity of application.
-
Type of sizing agent (starch, PVA, chitosan, or synthetic polymers) influences the balance between hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties.
Operators must monitor and adjust these factors to achieve optimal results. Advanced control systems in modern size presses and coating machines help maintain consistency and quality. By understanding and managing these variables, manufacturers produce paper that meets strict industry standards for strength, printability, and durability.
Environment
Eco-Friendly Options
Eco-friendly surface sizing agents have become a central focus in the papermaking industry. Manufacturers now prioritize natural materials such as tall oil rosin, wood rosin, starch-based agents, and cellulose derivatives like hydroxyethyl cellulose. These agents offer strong performance while reducing environmental impact. The market for these sustainable solutions continues to expand, driven by consumer demand and regulatory pressures.
|
Aspect |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Eco-friendly Surface Sizing Agents |
Tall oil rosin, wood rosin, starch-based agents, cellulose derivatives (e.g., hydroxyethyl cellulose) |
|
Market Size (2025) |
|
|
Market Size (2030 Projection) |
Over USD 5 billion |
|
Market Growth Drivers |
Sustainability trends, regulatory pressures, demand for sustainable packaging and paper products |
|
Emulsion Type Agents |
Growing rapidly due to eco-friendly appeal |
|
Key Companies |
BASF SE, Dow Inc., Evonik Industries AG, Arkema S.A., Solvay S.A., Eastman Chemical Company, Ashland Global Holdings Inc., Kemira Oyj, Sika AG, Clariant AG |
Emulsion-type agents now account for 45% of the total market share, reflecting their rapid growth and eco-friendly reputation. The global market revenue reached USD 3.5 billion in 2024 and is projected to climb to USD 5.2 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate of 5.1%. Consumer trends also reveal that 74% of buyers are willing to pay more for sustainable packaging, highlighting the importance of green chemistry in papermaking.
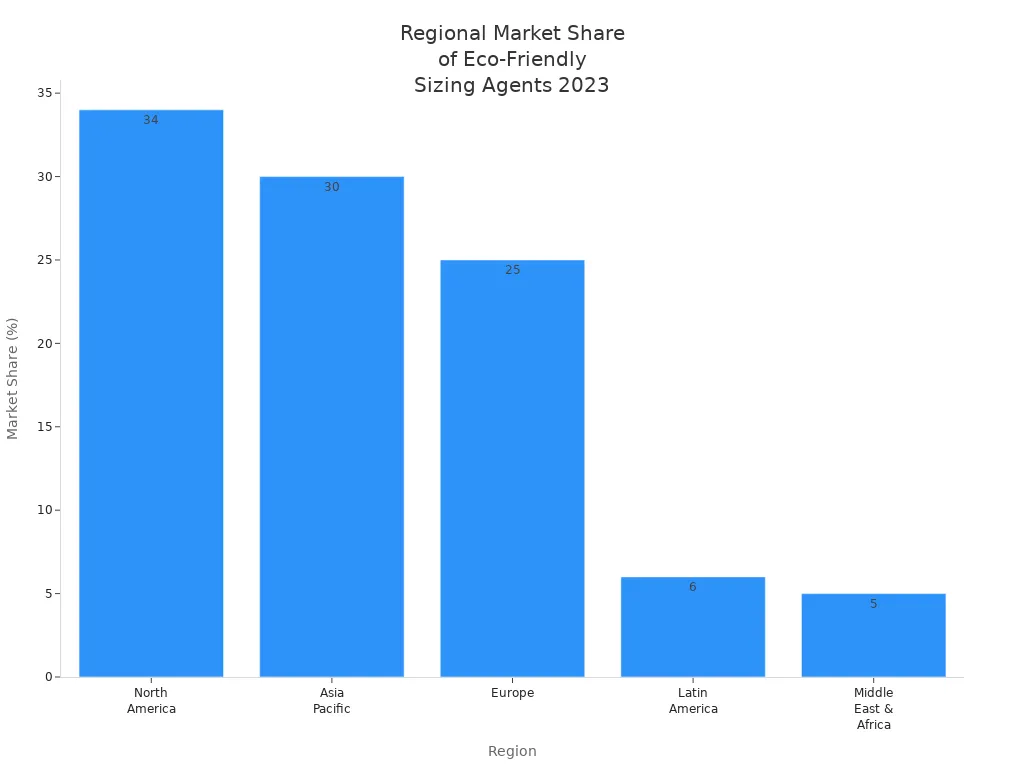
Regulations
Regulatory frameworks shape the development and adoption of surface sizing agents worldwide. The European Union enforces the EU Green Deal and REACH chemical restrictions, which require low volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and recyclable products. These rules have increased the use of water-based and bio-based enhancers, even as production costs rise by 12–18%. In China, the Dual Carbon Policy and strict recycling targets drive the adoption of nano-cellulose additives and green packaging initiatives. North America’s California Proposition 65 and EPA Tier IV standards push companies to reformulate products and invest in recycled paper-compatible enhancers.
|
Region |
Sustainability Initiative / Regulation |
Impact on Surface Sizing Agents Development and Adoption |
Examples / Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
European Union |
EU Green Deal, REACH chemical restrictions |
Mandates low VOCs, recyclable products; drives shift to water-based, bio-based enhancers; increases production costs |
Bio-based starch and lignin derivatives make up 38% of EU market; price premiums accepted in Germany and Scandinavia |
|
China |
Dual Carbon Policy, recycling targets |
Drives demand for enhancers improving recycled fiber strength; rapid growth in nano-cellulose production |
Adoption of nano-cellulose additives; government-led green packaging initiatives |
|
North America |
California Proposition 65, EPA Tier IV standards |
Requires reformulation to meet stricter toxicity thresholds; large R&D investment in recycled paper-compatible enhancers |
Increased use of AKD and bio-based agents; 68% recycled paper utilization rate |
Sustainability
Sustainability initiatives now influence every stage of surface sizing agent development. Leading companies such as BASF SE and Kemira Oyj invest in bio-based and polymer chemistries to meet market and regulatory demands. BASF’s HydroSize platform improves paper strength and water repellency while reducing environmental impact. Kemira’s FennoStrength series uses starch and lignin derivatives to enhance surface smoothness and lower chemical oxygen demand in wastewater. Their research and development pipelines include enzyme-assisted treatments that reduce energy consumption.
-
The American Forest & Paper Association reports growing demand for green paper products, which fuels investment in sustainable chemistries.
-
The natural sizing agents segment, especially starch- and cellulose-based products, is projected to grow fastest due to regulatory support and consumer preference.
-
Asia Pacific leads the market, with government initiatives like China’s Green Packaging Initiative promoting bio-based sizing agents.
-
North America’s EPA encourages the adoption of bio-based and AKD sizing agents, supporting innovation and market expansion.
Sustainability efforts also address energy efficiency. In Africa, carbon tax policies incentivize the use of enzymatic surface-sizing agents, which can reduce energy use by up to 20%. However, limited infrastructure in emerging markets slows adoption. As sustainability becomes a global priority, the papermaking industry continues to innovate, ensuring that surface sizing agents support both environmental goals and high-performance paper products.
Challenges
Application Issues
Surface sizing agents present several application challenges in modern papermaking. Operators must address these issues to ensure consistent paper quality and production efficiency.
Coating Defects
Coating defects often arise during the application of surface sizing agents. These defects can include uneven distribution, streaks, or blotches on the paper surface. Several factors contribute to these problems:
-
Inconsistent dispersion of sizing agents across the sheet.
-
Variability in paper pore size and density, which affects how the agent penetrates.
-
Premature decomposition of sizing agents before proper curing.
-
Inadequate drying or curing, which reduces the effectiveness of the sizing layer.
-
Interactions with minerals and additives, such as alum or cationic starch, that can alter sizing performance.
Operators must monitor the process closely. They often use mechanical and printability tests to verify that the paper maintains sufficient surface strength for downstream printing.
Foaming
Foaming represents another frequent challenge during surface sizing. When air becomes trapped in the sizing solution, foam can form and disrupt the application process. This leads to:
-
Poor retention of sizing agents on the paper surface.
-
Irregular coating thickness and surface defects.
-
Increased risk of machine stoppages and maintenance needs.
Manufacturers often add defoamers or adjust process parameters to control foaming. However, balancing these adjustments without compromising paper quality requires skill and experience.
Note: The choice of sizing agent, pH, and temperature can influence both coating defects and foaming tendencies. Each type of agent—such as ASA, AKD, or rosin—may respond differently under varying conditions.
Cost vs. Performance
Papermakers constantly weigh the cost of surface sizing agents against their performance benefits. Starch-based agents offer affordability and sustainability but may lack the water resistance needed for demanding applications. Synthetic agents like AKD and ASA provide superior durability and printability, yet they come at a higher price. The retention efficiency of these agents during application also affects overall costs. If the sizing agent does not adhere well or decomposes prematurely, waste increases and production costs rise. Achieving the right balance between cost and performance remains a key challenge, especially as market demands shift toward higher-quality and more sustainable paper products.
|
Sizing Agent Type |
Cost |
Performance |
Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Starch-Based |
Low |
Moderate |
General printing, eco-friendly |
|
Synthetic (AKD/ASA) |
High |
High |
Packaging, specialty papers |
Innovations
Recent years have seen significant innovation in surface sizing agents. The industry has shifted from traditional materials like starch and rosin to advanced synthetic agents such as AKD and ASA. These new agents deliver improved water resistance, durability, and printability. Manufacturers now focus on eco-friendly, biodegradable, and renewable sizing agents that support recycling and reduce environmental impact. For example, a water-soluble dual-component agent based on lignin derivatives—sodium lignosulfonate and polyamic acid—has emerged. This bio-based agent enhances adhesion between fibers and polymers, boosting flexural and interlaminar shear strength by nearly 30%. Hybrid strategies that incorporate nanoparticles also show promise for further improving mechanical properties, though controlling nanoparticle dispersion remains a technical hurdle. These innovations not only improve paper quality but also help reduce waste and support cost-effective, sustainable manufacturing.
Tip: Sustainable sizing agents not only benefit the environment but also enhance production efficiency and paper performance, making them a smart investment for the future of papermaking.
Surface sizing agents remain essential for producing high-quality, durable, and sustainable paper. Recent studies show that biodegradable agents like CMC improve paper strength, printability, and environmental performance.
-
Manufacturers now focus on bio-based and application-specific solutions.
-
Over 180 new products launched in 2023 highlight green chemistry and improved bonding.
-
Cold-water AKD dispersions and nano-sizing technology reduce energy use and enhance barrier properties.
-
These innovations support the shift to sustainable packaging and meet strict regulations.
-
The market is projected to reach USD 5.2 billion by 2033, driven by demand for eco-friendly paper products.
FAQ
What is the main function of a surface sizing agent in papermaking?
Surface sizing agents improve paper’s surface strength, printability, and resistance to water. They form a protective layer on the paper, which helps inks stay on the surface and prevents liquid penetration.
How do surface sizing agents differ from internal sizing agents?
Surface sizing agents apply to the paper’s exterior after sheet formation. Internal sizing agents mix into the pulp before sheet formation. Surface sizing mainly affects printability and water resistance at the surface, while internal sizing impacts the entire sheet.
Are surface sizing agents safe for food packaging?
Most modern surface sizing agents meet food safety standards. Manufacturers use food-grade or bio-based agents for food packaging. Always check for compliance with local regulations and certifications.
Can surface sizing agents improve recycled paper quality?
Yes. Surface sizing agents enhance fiber bonding and surface strength in recycled papers. They help reduce dusting and improve print quality, making recycled paper more suitable for demanding applications.
What are the most eco-friendly surface sizing agents?
Starch-based and cellulose-derived agents offer the best eco-friendly profiles. These agents come from renewable resources and biodegrade easily. Many manufacturers now focus on these options to meet sustainability goals.
How do manufacturers measure the effectiveness of surface sizing?
Manufacturers use tests like Cobb, Stöckigt, and contact angle measurements. These tests evaluate water absorption, ink penetration, and surface hydrophobicity. Results help ensure the paper meets industry standards.
Do surface sizing agents affect paper recyclability?
Most surface sizing agents do not hinder recyclability. Bio-based and water-soluble agents support recycling processes. Synthetic agents may require special handling, but modern formulations aim to minimize environmental impact.
Tip: Always consult technical data sheets for recyclability and environmental information.
Ready to Improve Your Paper’s Surface Strength and Printability?
👉 Explore Our Surface Sizing Solutions






